Emerging technologies are in a constant state of innovation and evolution. Accordingly, our manifesto is a living document. It was last updated on February 6, 2018.
The Decentralization Revolution
For the first time in history, technologies have converged that enable humanity to make progress on a scale never before seen. Blockchain Technology Research Innovations Corporation (BTRIC), a US-based 501(c)(3) charitable organization was founded to identify, research, develop, and foster the technologies and projects – some that already exist, and some that will emerge in the future – that will usher in this revolution in modern society.
Throughout much of history, and up to the present day, centralized systems of power and control hold enormous influence over various aspects of our lives. These systems of power are controlled by the few in a centralized way. Gatekeepers of power rely on having structures of control to continue their opaqueness, unaccountability, corruption, inefficiency, nepotism, and stagnation. This has been going on for thousands of years and it has been no different in the last century with our corporations, banks, and governments.
In the past, some of this centralization was necessary. For example, the only way to get information in a pre-telegraph era was from leaflets and newspapers. Depending on where a person lived, they may only have access to “stale” information many days or weeks old. These early information sharing mediums were limited to those who could physically get their hands on a copy, or have it read to them (and literacy rates in those times were only a fraction of what they are today). Telegraphs and telephones increased the speed at which information could travel from point A to B, which helped increase the timeliness of long-distance communications – newspapers could become more relevant and rapid person to person long-distance communication became possible. Radio and television broadened the size of the audience significantly and allowed for information to be disseminated to large numbers of people at once.
However, unfortunately today’s society is rife with instances of abuse of this centralized power and control. Around the world, governments have been corrupted by dominant corporations working in concert with information providers to maintain their mutual control over public discourse. Monetary authorities have abused their power to manipulate markets, put nations in debt to the tune of many trillions of USD, and favor the small few at the expense of the many. Thinking about it, with control over information flow, this wasn’t that hard to accomplish.
Instant, worldwide communication holds the potential to change the paradigm in a spectacular and disruptive manner. The emergence of the Internet began this process, allowing billions of people to spread their message, build their business, or increase awareness of their cause or belief. People can, in virtual space, gather, exchange information, socialize, and work on projects of many different types. The Internet has changed businesses and business-models as well, one example being the recording industry, which used to charge $20 USD for a compact disc (of which only a tiny fraction was earned by the composers and artists). This business had to adapt to market dynamics and adjust their practices, as the proliferation of file-sharing services caused serious impact to their legacy business model.
Times have changed. We now live in a world with instant, worldwide communication. Mediums such as Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube have shown that anyone, anywhere can spread information to millions of people, pretty much instantly. This is enormously powerful and revolutionary. It has never truly been possible before in human history. However, even the Internet, as it currently exists, has centralized controllers. These are large corporations, such as Apple, Facebook, Amazon, Twitter, and Google – including its YouTube brand. They have been shown to exert significant power over what they choose to allow on their platforms. This is their right – after all, it’s their platform – but is it what is right for society? We know that they only share a small amount of the revenue they make with the people that are publishing the content on their platforms. Some even accuse them of censorship and spreading of propaganda. More commonly, it has been observed that manipulation of search results or content display has been done to influence ad revenues. Some companies have even been forced to restate their earnings as these abuses have become known. Governments are censoring (or forced these and other platforms to self-censor) content that is “controversial”, as are other powerful special interests. The platforms themselves are large corporations and have been shown to censor content that does not comport with their agenda.
Much of the world has moved from a silo of “traditional media” to “new media” as the source of their news and information. The problem is the silo. So long as content providers control what you see, and what you don’t, they hold enormous sway over the public discourse. A fair society requires open, uncensored access to all sources of information. Of course, illegal and obscene content should be moderated, but no central authority is necessary for that.
The Promise of Decentrlization
Decentralization is a big part of the solution to this problem. Imagine – instead of one large YouTube run by Google that stores all of the video content, a thousand or even ten thousand small “YouTubes” – nodes on a decentralized video platform, with no central point of control or censorship, with full redundancy, and more efficiently using resources that otherwise would be idle. Each of these nodes talks to and shares content and users with all of the others, yet none can censor the other. Community-based rules could be implemented that require some type of consensus for content moderation. If enough people flag a video as being obscene, it’s hidden. Higher, trusted moderators can double check those decisions to ensure they weren’t censored for an inappropriate reason. Each time the a user’s moderation flag decision agrees with the trusted moderators, their “moderation accuracy” increases, and therefore next time, they will hold more sway in the level of consensus required to hide an individual video. Dynamic systems, controlled by software rules and consensus – not personalities, politics, or ideology.
Today we see decentralization beginning to show the real power to do away with an institution as old as recorded history itself, banking. Since the time of the money changers, banks have held control over people, businesses, even whole countries. Bitcoin demonstrated that much of what banks do can be done more fair, more efficiently, and direct – with no middleman – through the blockchain, the most common type of consensus-based distributed ledger technology. Over a thousand other cryptocurrencies exist. Some are simple clones, but some demonstrate novel technologies that could eventually gain widespread adoption. Traditional financial institutions will not be able to keep up with the rate of technological innovation. Cryptocurrencies have already proven the power to store wealth in a way that cannot be tampered with by a body such as the Federal Reserve or a government. Unlike fiat currencies, cryptocurrency, when properly implemented, cannot be debased.
In many ways, the emerging technologies that will shape our future are arriving at a crucial time in world history. People are less trustful of banks, governments, corporations, and the media than ever before – and for good reason. The curtain is being pulled back before their eyes, and the levers of control exerted over society for so many centuries are laid bare for all to see. People have known this before, but had no effective way to combat it at scale.
The Internet changes everything. The Decentralization Revolution has arrived, and it’s not going anywhere but to the moon. These technologies, the most important among them being consensus-based distributed ledger technology, will change the world in ways that were never before possible. They hold the promise of a future with greater accountability, equality, and efficiency and a modern society that is much more fair, much more open, and much more honest. There has never been a time before where it was possible to change the world in the ways that now are happening.
- The silos will become open, distributed networks, where arbitrary censorship is impossible and users have full control over their own data.
- The gatekeepers, powerful people, and corporations that control the flow of information will be gone, replaced with structures to promote good people and great ideas. May the best idea win!
- Wealth will be distributed more fairly to everyone, through true free-market capitalism, not oligarchy or socialism.
- Rigging the system will become impossible as technology renders “points of rigging” nonexistent.
- The tactics that have been used to divide people – based on gender, religion, race, national origin – will be overcome by fair, immutable records and decisions based on rules agreed upon by consensus.
- Even democracy itself may be reshaped, modernized into a more fluid construct where more power is held directly in the hands of the many. Certainly, more factual information, something that is necessary for the health of a democracy, will be available without gatekeepers constraining it.
Power to the people. Power to each individual. Decentralize the world.
Overview of Selected Emerging Technologies
Consensus-based Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
The foundational technology enabling this revolution is consensus-based distributed ledger technology (DLT). The most common type of distributed ledger technology in use today is blockchain, but there are other variants of distributed ledger, including a proprietary technology called “Hashgraph” as well as directed acyclic graph. All of these technologies allow for data to be stored immutably and distributed to a large number of participants, each of which validates the data as authentic using consensus-making rules. Because each node in the distributed system is using software that validates incoming transactions and applies the same rules, DLT allows trust to be placed in the software and network, instead of the counterparty.
The most widely used application today of DLT is in cryptocurrency, but its potential extends well beyond that. Broadly implemented in many diverse fields, this type of peer-to-peer distributed system has immense potential to render largely obsolete centralized “choke-points” that have slowed human progress. This powerful technology, enabling decentralization and trust-free transactions, can be extended into use well beyond digital currencies. Many applications can benefit from trustless yet immutable records of transactions. These include authentication of intellectual property rights, traceability of products in commerce, equity and commodities trading, and many more.
For example, a sufficiently developed DLT based stock exchange could be operated peer-to-peer, without any brokers or underwriters. A company could issue shares of stock that would be transacted through DLT, facilitating the initial issuance as well as all future transactions of each share. The entire record of transactions would be shared across all of the nodes in the system, allowing full transparency and no possibility of fraudulent transactions.
Trust the code and the consensus rules it enforces. Trust consensus-based distributed ledger technology.
Cryptocurrency and tokens
Bitcoin (BTC) is the most widely recognized application of blockchain. Bitcoin is a worldwide cryptocurrency and digital payment system called the first decentralized digital currency, as the system works without a central repository or single administrator. It was created by an anonymous person or group of people that communicated under the pseudonym of Satoshi Nakamoto, and released as open-source software in 2009. Bitcoin exists outside of the control of any government, any corporation, or any other entity. As of December 31, 2017, 1 BTC had a value of $14,156.40 USD, with a total market capitalization of $237.4 billion USD. The value of Bitcoin has grown immensely as it is recognized as a reliable and independent store of value and medium of exchange. This growth is despite the fact that less than 1% of the world’s population have ever possessed any Bitcoin. It is widely expected that growth in Bitcoin will continue as adoption increases.
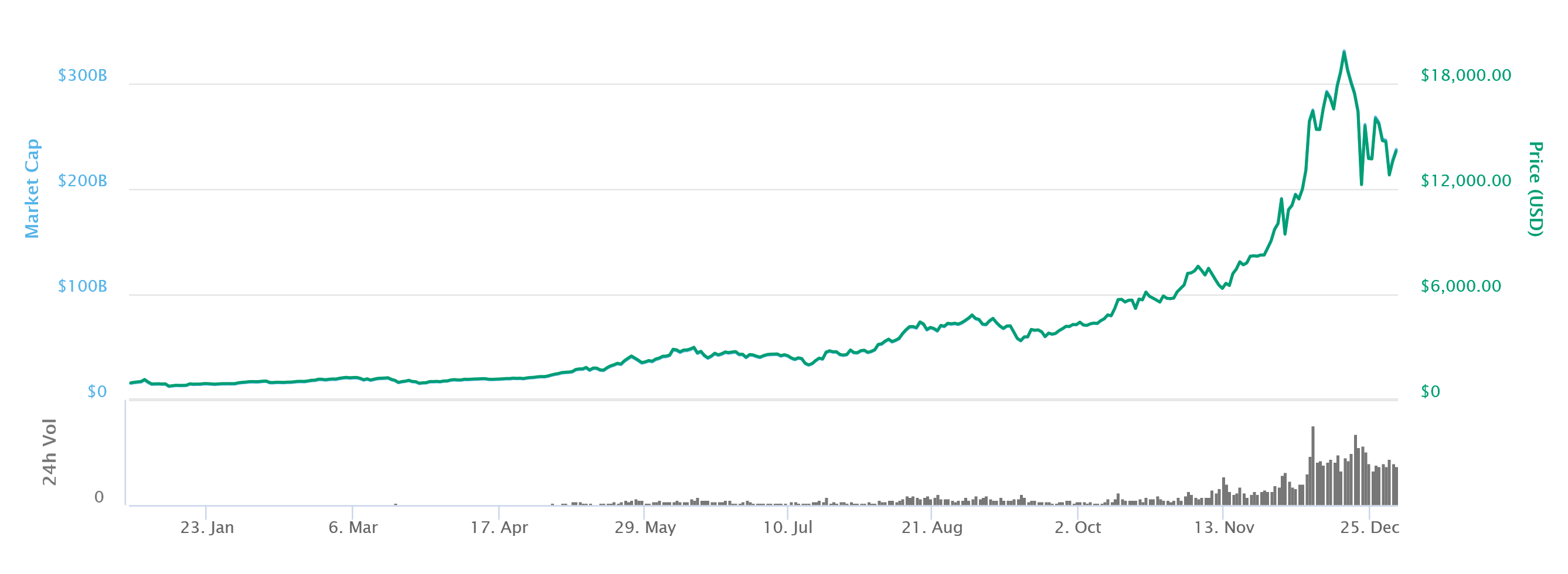
Bitcoin Price Chart (2017)
Many other cryptocurrency projects have been created, inspired by the success of Bitcoin. Some of these projects have been simple “clones”, adding little to the ongoing progress of cryptocurrency development. However, other projects, such as Ethereum, have contributed significant innovation in the field. Enabling and fostering innovation is good for the ecosystem as a whole, as it allows concepts to be developed and refined that may provide solutions to challenges that have been identified. In the cryptocurrency ecosystem, challenges that are currently being tackled include the reliance on centralized exchanges, the high (as compared to a credit card transaction) learning and usability curve, the difficulty of scaling transaction volumes and speeds to those needed for widespread adoption, and regulatory compliance.
The economies of the 21st century move at the speed of light. Only cryptocurrency delivers fair, immutable, and tamper-proof exchange of value without centralized control.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the connection of devices (other than typical fare such as computers and smartphones) to the Internet. Cars, kitchen appliances, and even heart monitors can all be connected through the IoT. This list will continue to grow.
At its essence, IoT enables smarter decisions to be made about things in the real-world. Electrical grids can be made much more efficient, traffic patterns more regulated.
For example, IoT could enable tractor trailer trucks to deliver cargo more efficiently by sharing information between themselves. Two trucks, both half full, going to Philadelphia? Inefficient; instead, they can share the load. UPS and FedEx already do this for their own fleets, IoT will let the entire trucking industry gain similar improvements in efficiency. A distributed ledger would ensure that each item to be shipped would be tracked, fully accounted for, and that the responsible parties would be properly compensated for sharing in the task, probably paid in cryptocurrency. It is easy to see how IoT can increase efficiency and flexibility in scales that were not possible before.
IoT includes specialized hardware, such as telemetric sensors, commodity hardware, such as microcomputers, and software to coordinate and orchestrate the efficient operations of complex real-world systems. The opportunities in IoT are as diverse as the world we live in. Especially in the developing world, where trucks are not as plentiful and fuel is expensive and hard to obtain, IoT will enable people, communities, and countries to modernize their worlds faster than the current industrial nations could.
Technological innovation and advancement is a positive feedback loop. IoT brings efficiency and accuracy on a scale never before possible.
Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR)
Virtual and Augmented Reality are two complimentary technologies that have potential to change how people interact with computing devices.
Virtual reality (VR) is an artificial, computer-generated simulation or recreation of a real life environment or situation. It immerses the user by making them feel like they are experiencing the simulated reality firsthand, primarily by stimulating their vision and hearing. VR is typically achieved by wearing a headset like Facebook’s Oculus equipped with the technology, and is used prominently in two different ways:
- To create and enhance an imaginary reality for gaming, entertainment, and play (such as video and computer games, or 3D movies, head mounted display); and
- To enhance training for real life environments by creating a simulation of reality where people can practice beforehand (such as flight simulators for pilots).
Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that layers computer-generated enhancements atop an existing reality in order to make it more meaningful through the ability to interact with it. AR is developed into apps and used on mobile devices to blend digital components into the real world in such a way that they enhance one another, but can also be told apart easily. AR technology is quickly coming into the mainstream. It is used to display score overlays on telecasted sports games and pop out 3D emails, photos or text messages on mobile devices. Some overview facts about AR are:
- The 2016 pop culture phenomenon known as “Pokémon Go” was a form of AR technology, where virtual characters appeared, using geolocation, in real-world places; and
- AR technology has uses beyond gaming and entertainment, and can be used to receive information from and give information to computer systems in a more immersive manner than current technologies.
The potential applications of VR/AR go beyond entertainment, and can also be used to simulate real-world exercises including applications in military, law-enforcement, medicine, and science. It has been shown that virtually “going inside” of a human body, through a simulation, can provide medical insights that were difficult to discover in other ways. Potential applications exist when combined with advanced sensing technology to virtually “place people” where they otherwise could not go, for tactical planning, scientific exploration, and, indeed, entertainment and educational purposes.
Beyond keyboards, mice, and screens. Virtual and Augmented reality redefines the interface between humans and machines.
Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning (AI/ML/DL)
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) are three different levels an overarching goal, focusing on technology to think and act like humans do. The application of these technologies enables interaction with computers in a more intuitive ways, as well as enabling those systems to detect patterns, analyze large data sets, and ultimately to actually “think”, making informed decisions based on data as well as the computer’s memory of past experiences. AI, ML, and DL are often used interchangeably, especially in the realm of big data. But these aren’t the same thing, and it is important to understand how these can be applied differently.
Artificial intelligence is a broader concept than machine learning, which addresses the use of computers to mimic the cognitive functions of humans. When machines carry out tasks based on algorithms in an “intelligent” manner, that is AI.
Machine learning is a subset of AI and focuses on the ability of machines to receive a set of data and learn for themselves, changing algorithms as they learn more about the information they are processing. Training computers to think like humans is achieved partly through the use of neural networks. Neural networks are a series of algorithms modeled after the human brain. Just as the brain can recognize patterns and help us categorize and classify information, neural networks do the same for computers. The brain is constantly trying to make sense of the information it is processing, and to do this, it labels and assigns items to categories. When we encounter something new, we try to compare it to a known item to help us understand and make sense of it. Neural networks do the same for computers. Some of the benefits of using ML neural network technology are:
- Extraction of meaning from complicated data;
- Detection of trends and identification of patterns too complex for humans to notice;
- Learning by example; and
- Processing of information much faster than humans.
Deep Learning goes yet another level deeper and can be considered a subset of machine learning. The concept of DL is sometimes just referred to as “deep neural networks,” referring to the many layers involved. A neural network may only have a single layer of data, while a deep neural network has two or more. The layers can be seen as a nested hierarchy of related concepts or decision trees. The answer to one question leads to a set of deeper related questions. DL works best when it has a large dataset to be trained. Instead of being programmed with the edges that define items, the systems learn from exposure to millions of data points. An early example of this is the Google Brain learning to recognize cats after being shown over ten million images. Deep learning networks do not need to be programmed with the criteria that define items; they are able to identify edges through being exposed to large amounts of data.
More intelligent technology improves humanity by making it easier, and faster, than ever before to find the “signal” in the “noise”.
Content Creator Control and Personal Data Store (CCC/PDS)
As more information about people and businesses are stored and aggregated online, there is a growing recognition that people want more control over their own content. Social media illustrates the example of a person posting an embarrassing post or photo and it being essentially “part of the Internet” forever. Content Creator Control and Personal Data Store are two concepts that focus on improving the balance between content creators and content aggregators.
Large platforms such as YouTube depend on creative (and sometimes, not so creative) users to post videos to their platform. These videos are then monetized by selling advertisements. Some content creators get a slice of that monetization. Most do not. Even those that do only get a small fraction of the revenues generated. Content Creator Control is about developing new platforms that give the content creators more control over the use of their content, and ultimately a better share of the revenues. In addition, CCC platforms are being designed that are decentralized, so that they cannot be controlled or censored by any single entity. Moderation methods can be based on consensus, not political ideology. CCC platforms, while still young, hold the potential to obsolete “silo” based methods of storage of rich data. They also have the power to revolutionize and decentralize search engines, which, is currently a huge business for just a small handful of large corporations globally.
PDS technology, on the other hand, allows a user to control key identifying information, including social connections, contact information, and other personal information in a manner that is under the users own control, delegating it from a secure store to only those parties or services the user chooses. As is often said on the Internet, “If you’re using a website for free, you are the product”. PDS has the potential to change some of the commercial exploitation of user’s personal information, browsing habits, social or geo-located connections, etc.
End the gatekeepers who have censored information. Break down the walls that cause divisiveness, while maintaining more control over your private information.
Summary
The technologies that have potential to reshape society for centuries to come have emerged, with more to come. Surely, 100 years from now, all of them will look very different than they do today. However, if we do not make the most of this opportunity – unique with respect to economic, social, and technological developments – to develop these technologies to the benefit of humanity, others will seize control of them, either by sequestration, or by subversion.
Let’s work together to build great businesses that reinvent humanity.


